Introduction
- Raspberry Pi is a series of small single-board computers developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in collaboration with Broadcom.
- It is affordable, compact, and versatile, making it popular for education, DIY projects, and professional applications.
- Initially created for teaching basic computer science, it has gained widespread use in projects like gaming devices, fitness gadgets, weather stations, and more.
- Manufactured mainly in the Sony factory, Pencoed, Wales.
Generations and Models
- First launched in 2012, Raspberry Pi has multiple generations: Zero, 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- Model types:
- Model A & A+ → Compact, fewer ports, and lower cost.
- Model B & B+ → Full-sized, more ports, and better connectivity.
- Raspberry Pi Zero → The smallest and most affordable version.
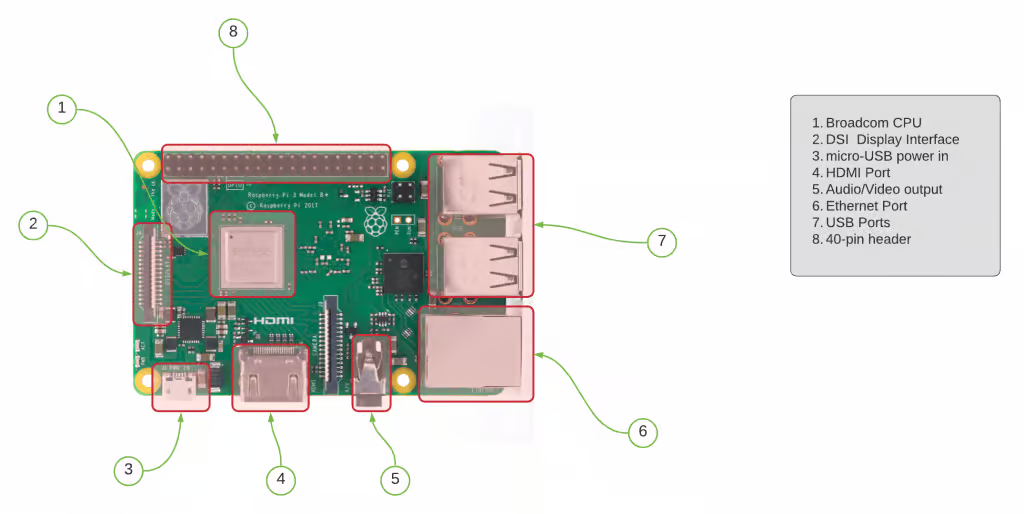
Raspberry Pi Versions & Specifications
| Version | Release Year | Size (mm) | CPU Speed | Cores | RAM | USB Ports | Power | HDMI | Wi-Fi | Bluetooth | Ethernet | External Storage |
| Raspberry Pi 4 Model B | 2019-2020 | 85.6 x 56.5 | 1.5 GHz | Quad | 1, 2, 4, 8 GB | 2 USB3.0 + 2 USB2.0 | 5.1V 3A (USB-C) | 2 × micro-HDMI (4K) | Dual Band (2.4 & 5GHz) | Bluetooth 5.0 | Gigabit Ethernet | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ | 2018 | 85.6 x 56.5 | 1.4 GHz | Quad | 1 GB | 4 USB2.0 | 5.1V 2.5A | HDMI, Composite (TRRS) | Dual Band (2.4 & 5GHz) | Bluetooth 4.2 | 10/100 Mbps | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model B | 2016 | 85.6 x 56.5 | 1.2 GHz | Quad | 1 GB | 4 USB2.0 | 5.1V 2.5A | HDMI, Composite (TRRS) | 2.4 GHz | Bluetooth 4.1 | 10/100 Mbps | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ | 2018 | 65 x 56.5 | 1.4 GHz | Quad | 512 MB | 1 USB2.0 | 5.1V 3A | HDMI, Composite (TRRS) | Dual Band (2.4 & 5GHz) | Bluetooth 4.2 | No Ethernet | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi Zero Wireless | 2016 | 65 x 30 x 5 | 1 GHz | Single | 512 MB | 1 MicroUSB | 5.1V 1.2A | Mini-HDMI, GPIO Composite | 2.4 GHz | Bluetooth 4.1 | No Ethernet | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi Zero | 2015 | 65 x 30 x 5 | 1 GHz | Single | 512 MB | 1 MicroUSB | 5.1V 1.2A | Mini-HDMI, GPIO Composite | No Wi-Fi | No Bluetooth | No Ethernet | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi 2 Model B | 2015 | 85.6 x 56.5 | 1.2 GHz | Quad | 1 GB | 4 USB2.0 | 5.1V 1.8A | HDMI, Composite (TRRS) | No Wi-Fi | No Bluetooth | 10/100 Mbps | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+ | 2014 | 85.6 x 56.5 | 700 MHz | Single | 512 MB | 4 USB2.0 | 5.1V 1.2A | HDMI, Composite (TRRS) | No Wi-Fi | No Bluetooth | 10/100 Mbps | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model B | 2012 | 85.6 x 56.5 | 700 MHz | Single | 512 MB | 2 USB2.0 | 5.1V 3A | PAL, NTSC, HDMI, RCA | No Wi-Fi | No Bluetooth | 10/100 Mbps | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model A+ | 2014 | 65 x 56.5 | 700 MHz | Single | 512 MB | 1 USB2.0 | 5.1V 700mA | HDMI, Composite (TRRS) | No Wi-Fi | No Bluetooth | No Ethernet | MicroSD |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model A | 2013 | 85.6 x 56.5 | 700 MHz | Single | 256 MB | 1 USB2.0 | 5.1V 700mA | PAL, NTSC, HDMI, RCA | No Wi-Fi | No Bluetooth | No Ethernet | MicroSD |
Key Features





History & Development
- Founded in 2006 by Eben Upton, Pete Lomas, and David Braden.
- Goal: To create an affordable computer for learning and experimentation.
- Milestones:
- 2012: First Raspberry Pi (Model B) launched.
- 2013: Model A introduced (cheaper, less power).
- 2014-2015: Compact Model A+ and Raspberry Pi Zero released.
- 2019-2020: Powerful Raspberry Pi 4 with 8GB RAM and dual HDMI introduced.
- Why the name?
- "Raspberry" follows the tradition of naming computers after fruits.
- "Pi" refers to Python Programming Language.
Applications




