The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected physical devices that collect, process, and exchange data. These devices rely on IoT-supported hardware platforms, which provide the necessary components for connectivity, computation, and control.
IoT hardware platforms include microcontrollers, microprocessors, sensors, actuators, and communication modules that allow devices to interact with their surroundings and transmit data over the internet. These platforms can be categorized based on their capabilities, power consumption, and intended applications.
Arduino is a prototype platform (open-source) based on an easy-to-use hardware and software. It consists of a circuit board, which can be programed (referred to as a microcontroller) and a ready-made software called Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment), which is used to write and upload the computer code to the physical board.
Features
The features of Arduino are listed below:
- Arduino programming is a simplified version of C++, which makes the learning process easy.
- The Arduino IDE is used to control the functions of boards. It further sends the set of specifications to the microcontroller.
- Arduino does not need an extra board or piece to load new code.
- Arduino can read analog and digital input signals.
- The hardware and software platform is easy to use and implement.
Pin Diagram of Arduino
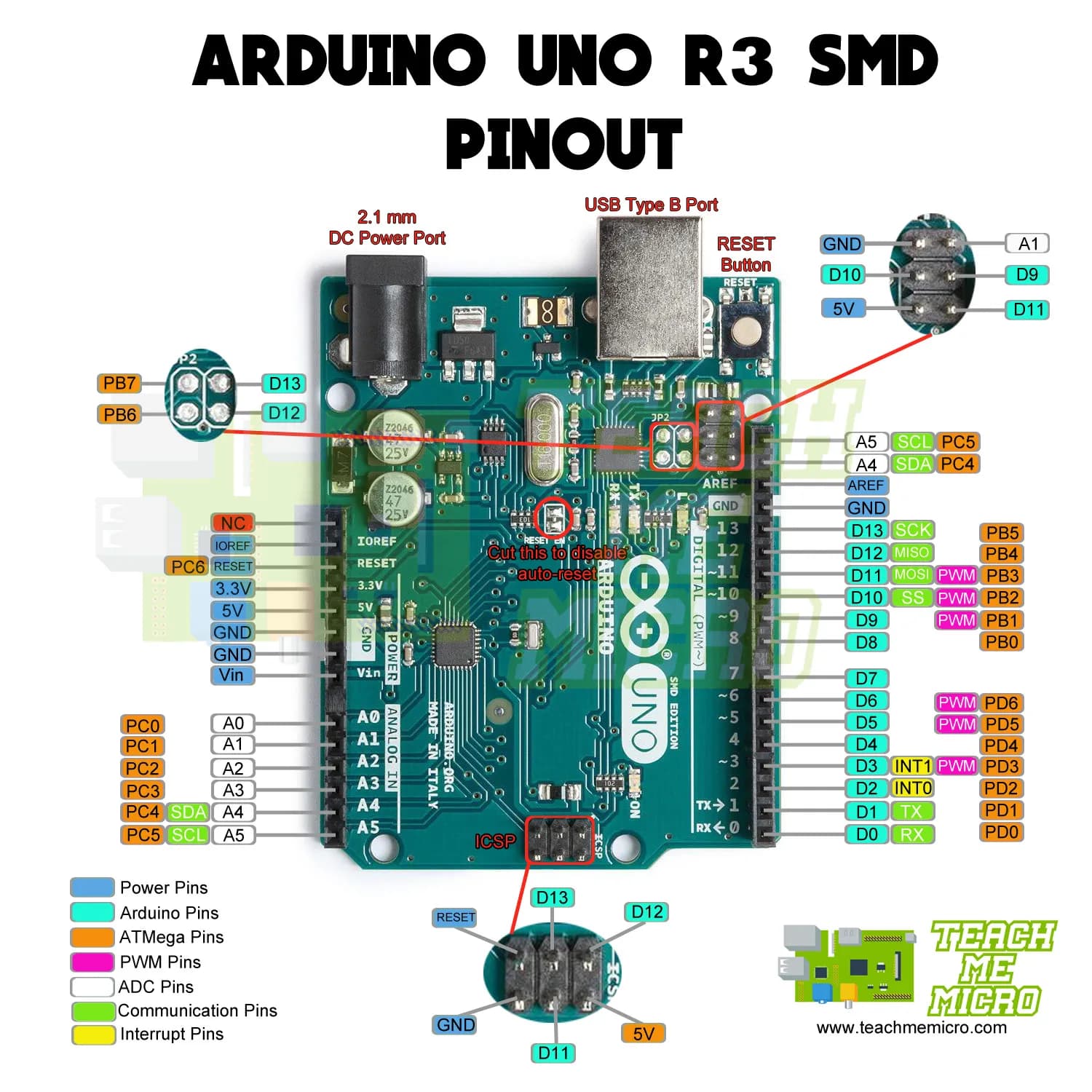
| Component | Description |
| Power USB | Powers the board via USB connection. |
| Barrel Jack | Powers the board using an external power supply (AC adapter). |
| Voltage Regulator | Regulates and stabilizes the DC voltage for the board. |
| Crystal Oscillator | Provides the clock signal (16 MHz) for timekeeping. |
| Reset Button | Resets the board, restarting the program. |
| Pins (Power) | - 3.3V, 5V: Provides power output. |
| Analog Pins (A0 - A5) | Reads analog signals from sensors and converts them into digital values. |
| Main Microcontroller | The brain of the board, usually an ATmega328P IC. |
| ICSP Header | Used for programming the microcontroller directly. |
| Power LED Indicator | Lights up when the board is powered correctly. |
| TX & RX LEDs | Indicate data transmission (TX) and reception (RX) via serial communication. |
| Digital I/O Pins (0 - 13) | Used for input/output, controlling modules like LEDs, sensors, etc. |
| PWM Pins (~) | Digital pins with Pulse Width Modulation capability. |
| AREF (Analog Reference) | Sets an external reference voltage for analog inputs. |
Types of Arduino Boards
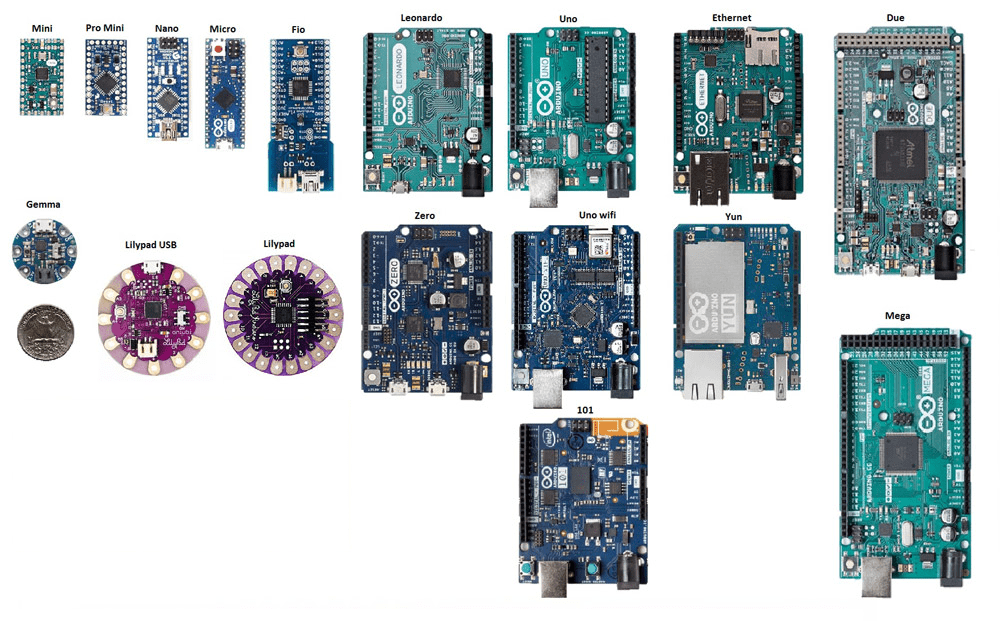
| Arduino Board | Microcontroller | Digital I/O Pins | Analog Pins | Special Features |
| Arduino UNO | ATmega328P | 14 | 6 | Most popular, easy for beginners |
| Arduino Nano | ATmega328P/ATmega168 | 14 | 8 | Small, compact, mini USB connectivity |
| Arduino Mega | ATmega2560 | 54 | 16 | More memory, 4 UARTs, ideal for larger projects |
| Arduino Micro | ATmega32U4 | 20 | 12 | Small, built-in USB connectivity |
| Arduino Leonardo | ATmega32U4 | 20 | 12 | Can act as a keyboard/mouse via USB |
| Arduino Due | Atmel SAM3X8E (ARM Cortex-M3) | 54 | 12 | 32-bit processor, higher performance |
| Arduino Lilypad | ATmega168/ATmega328 | 9 | - | Designed for wearable/e-textile projects |
| Arduino Bluetooth (BT) | ATmega168 | 16 | 6 | Wireless programming via Bluetooth |
| Arduino Diecimila | ATmega168 | 14 | 6 | USB-powered, earlier version of UNO |
| Arduino Robot | ATmega32U4 | Multiple | Multiple | Includes motors, sensors, display, and buttons |
| Arduino Ethernet | ATmega328 | 14 | 6 | Built-in Ethernet for IoT projects |
| Arduino Zero | ATSAMD21 (32-bit) | 14 | 6 | Debugging support, 32-bit extension of UNO |
| Arduino Esplora | ATmega32U4 | Predefined | Predefined | Has built-in sensors and joystick |
| Arduino Pro Micro | ATmega32U4 | 12 | 5 | Small form factor, similar to Arduino Mini |
Board Types
Various kinds of Arduino boards are available depending on different microcontrollers used. However, all Arduino boards have one thing in common: they are programed through the Arduino IDE.
The differences are based on the number of inputs and outputs (the number of sensors, LEDs, and buttons you can use on a single board), speed, operating voltage, form factor etc. Some boards are designed to be embedded and have no programming interface (hardware), which you would need to buy separately. Some can run directly from a 3.7V battery, others need at least 5V.
Here is a list of different Arduino boards available.
Arduino boards based on ATMEGA328 microcontroller
| Board Name | Operating Volt | Clock Speed | Digital i/o | Analog Inputs | PWM | UART | Programming Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino Uno R3 | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | USB via ATMega16U2 |
| Arduino Uno R3 SMD | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | USB via ATMega16U2 |
| Red Board | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | USB via FTDI |
| Arduino Pro 3.3v/8 MHz | 3.3V | 8MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| Arduino Pro 5V/16MHz | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| Arduino mini 05 | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 8 | 6 | 1 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| Arduino Pro mini 3.3v/8mhz | 3.3V | 8MHz | 14 | 8 | 6 | 1 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| Arduino Pro mini 5v/16mhz | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 8 | 6 | 1 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| Arduino Ethernet | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| Arduino Fio | 3.3V | 8MHz | 14 | 8 | 6 | 1 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| LilyPad Arduino 328 main board | 3.3V | 8MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| LilyPad Arduino simple board | 3.3V | 8MHz | 9 | 4 | 5 | 0 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
Arduino boards based on ATMEGA32u4 microcontroller
| Board Name | Operating Volt | Clock Speed | Digital i/o | Analog Inputs | PWM | UART | Programming Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino Leonardo | 5V | 16MHz | 20 | 12 | 7 | 1 | Native USB |
| Pro micro 5V/16MHz | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | Native USB |
| Pro micro 3.3V/8MHz | 5V | 16MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | Native USB |
| LilyPad Arduino USB | 3.3V | 8MHz | 14 | 6 | 6 | 1 | Native USB |
Arduino boards based on ATMEGA2560 microcontroller
| Board Name | Operating Volt | Clock Speed | Digital i/o | Analog Inputs | PWM | UART | Programming Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino Mega 2560 R3 | 5V | 16MHz | 54 | 16 | 14 | 4 | USB via ATMega16U2B |
| Mega Pro 3.3V | 3.3V | 8MHz | 54 | 16 | 14 | 4 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| Mega Pro 5V | 5V | 16MHz | 54 | 16 | 14 | 4 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
| Mega Pro Mini 3.3V | 3.3V | 8MHz | 54 | 16 | 14 | 4 | FTDI-Compatible Header |
Arduino boards based on AT91SAM3X8E microcontroller
| Board Name | Operating Volt | Clock Speed | Digital i/o | Analog Inputs | PWM | UART | Programming Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino Mega 2560 R3 | 3.3V | 84MHz | 54 | 12 | 12 | 4 | USB native |