1. What is Arduino?
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. It's widely used for prototyping electronic projects.
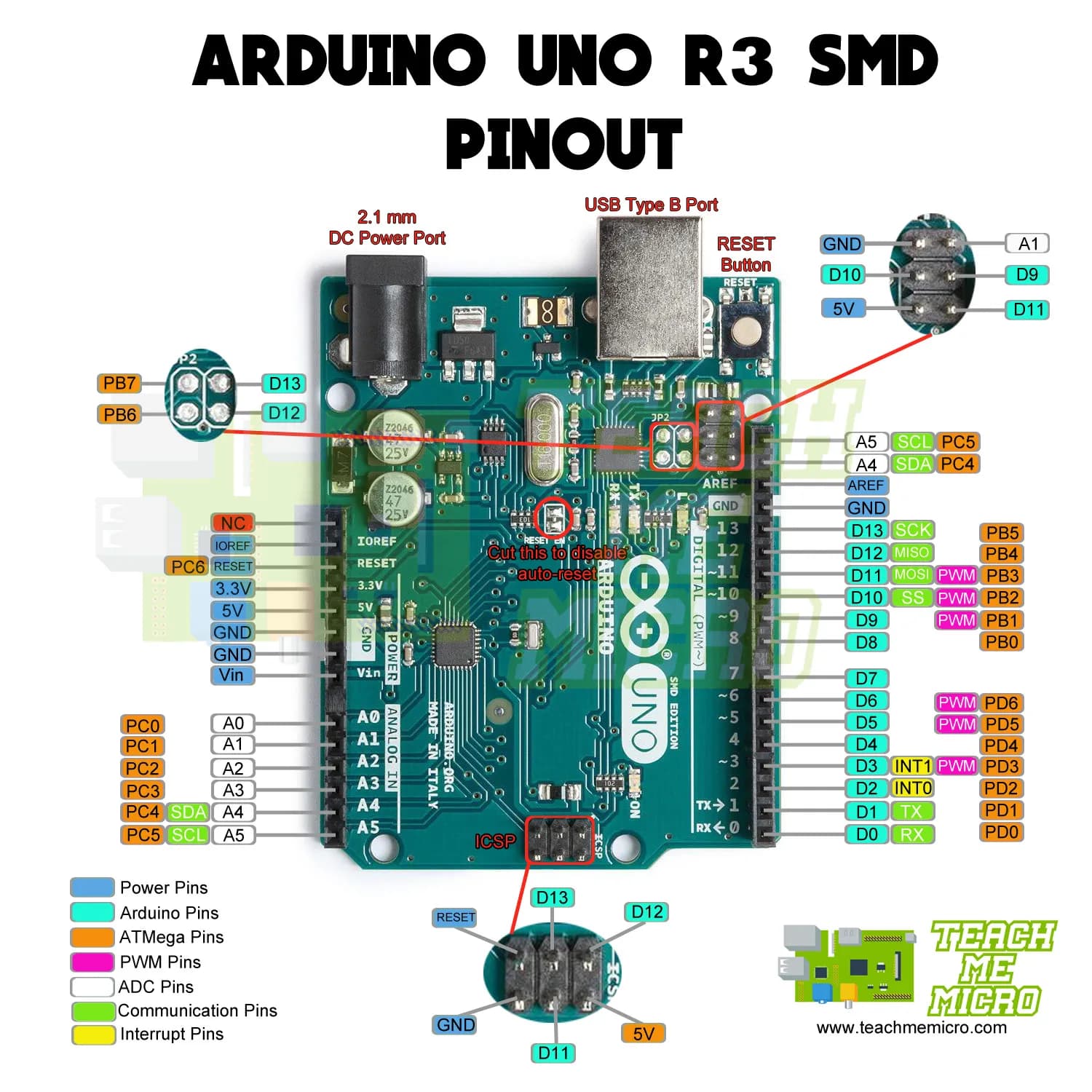
2. Basic Anatomy of an Arduino Board
Let’s take Arduino Uno as a reference (most commonly used board):
| Component | Description |
| 1. USB Port | Used to connect the Arduino board to a computer for programming and power. |
| 2. Power Jack | Allows external power supply (7V to 12V DC). |
| 3. Microcontroller | The “brain” of the board – usually ATmega328P. |
| 4. Digital I/O Pins | (0 to 13) Used for digital input/output operations. |
| 5. Analog Input Pins | (A0 to A5) Read analog sensors (0 to 1023 range). |
| 6. Power Pins | Includes 5V, 3.3V, GND (Ground), and Vin. |
| 7. Reset Button | Resets the board/program. |
| 8. TX/RX LEDs | Indicate communication via USB (Transmit & Receive). |
| 9. Voltage Regulator | Controls the voltage supplied to the board. |
| 10. Crystal Oscillator | Maintains time accuracy (usually 16 MHz). |
| 11. ICSP Header | Used to program the Arduino using external programmer. |
| 12. LED (Built-in) | Connected to pin 13, used for basic testing. |
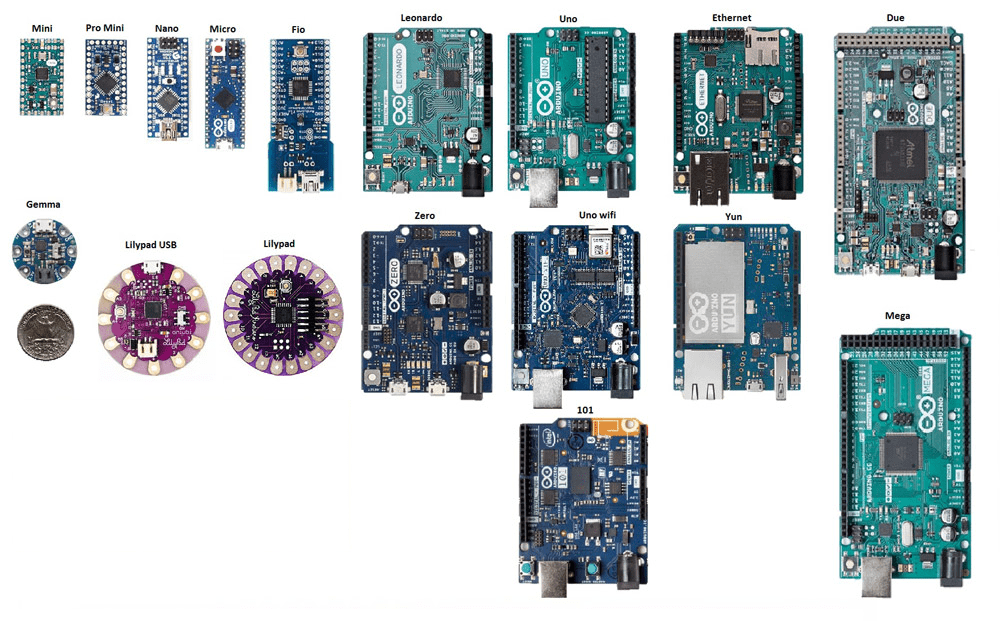
3. Common Arduino Boards
| Board | Microcontroller | Digital I/O Pins | Analog Pins | USB Type |
| Arduino Uno | ATmega328P | 14 | 6 | USB-B |
| Arduino Mega | ATmega2560 | 54 | 16 | USB-B |
| Arduino Nano | ATmega328P | 14 | 8 | Mini USB |
| Arduino Leonardo | ATmega32u4 | 20 | 12 | Micro USB |
4. Power Supply Options
- USB (from computer)
- External adapter (DC Jack)
- Batteries (via Vin pin or Jack)
5. Important Points
- Arduino is beginner-friendly.
- Code is written in Arduino IDE using C/C++.
- Programs written for Arduino are called “sketches.”
- Arduino is used in IoT, robotics, automation, and electronics education.